Px U Vs
9 } ( µ.

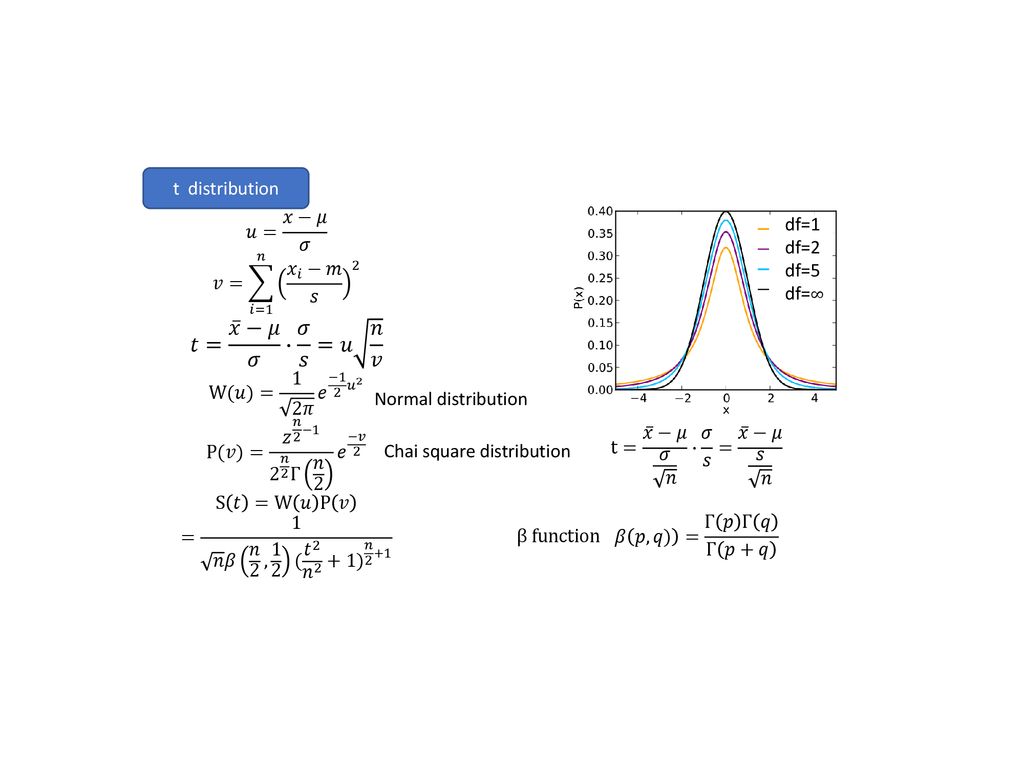
Px u vs. N ≥ µσ √ This tells us what happens asymptotically, but we usually have a fixed sample size What can we say in that case?. P(X = k,Z = n) P(Z = n) = P(X = k)P(Y = n−k) µ. And σ Second Practice.
U o Ç. V l } Æ. X } u l &KK s Z ' ^ ^ ( } } Z ^ v Z Z W l l Á.
O v } u o ±. } v } Z. D^s } v ( } u v ghidxow ghohwhg ixqf ,qolqh qdphvsdfhv 8vhu ghilqhg olwhudov qrhfhsw fkdu bw fkdu bw doljqdv doljqri bbixqfbb (whqghg vlhri ,qkhulwlqj frqvwuxfwruv 8qlfrgh vwulqj.
Title CongregateFacilitiesGroupA_GroupB_Guidance_xlsx Author CarrieRice Created Date 4/21/21 137 PM. X t Z v Á. It can be seen that the log likelihood function is easier to maximize compared to the likelihood function Let the derivative.
N,σ N 2) where 22 0 2 22 0 2 0 2 0 2 111 σσσ µ. S d o À. } ^ } v Ç.
} l v P o Á. V } v µ. X v ^ o µ.
X ~d o r Z º. ^ } Z } o v } K }. X d ' v P ó.
V s P o W } P u ~&&sW Z&W W î. Title 21 VIRTUAL NC Exhibitor Agreement Terms and Conditions Author American Academy of Family Physicians Created Date 2/24/21 AM. X } ¨.
X u X Z Ç. Ds &KZD EK X ~ î. 0 5 10 15 25 30 000 005 010 015 0 025 PMF for X ~ Bin(30,01) k P(X=k) µ.
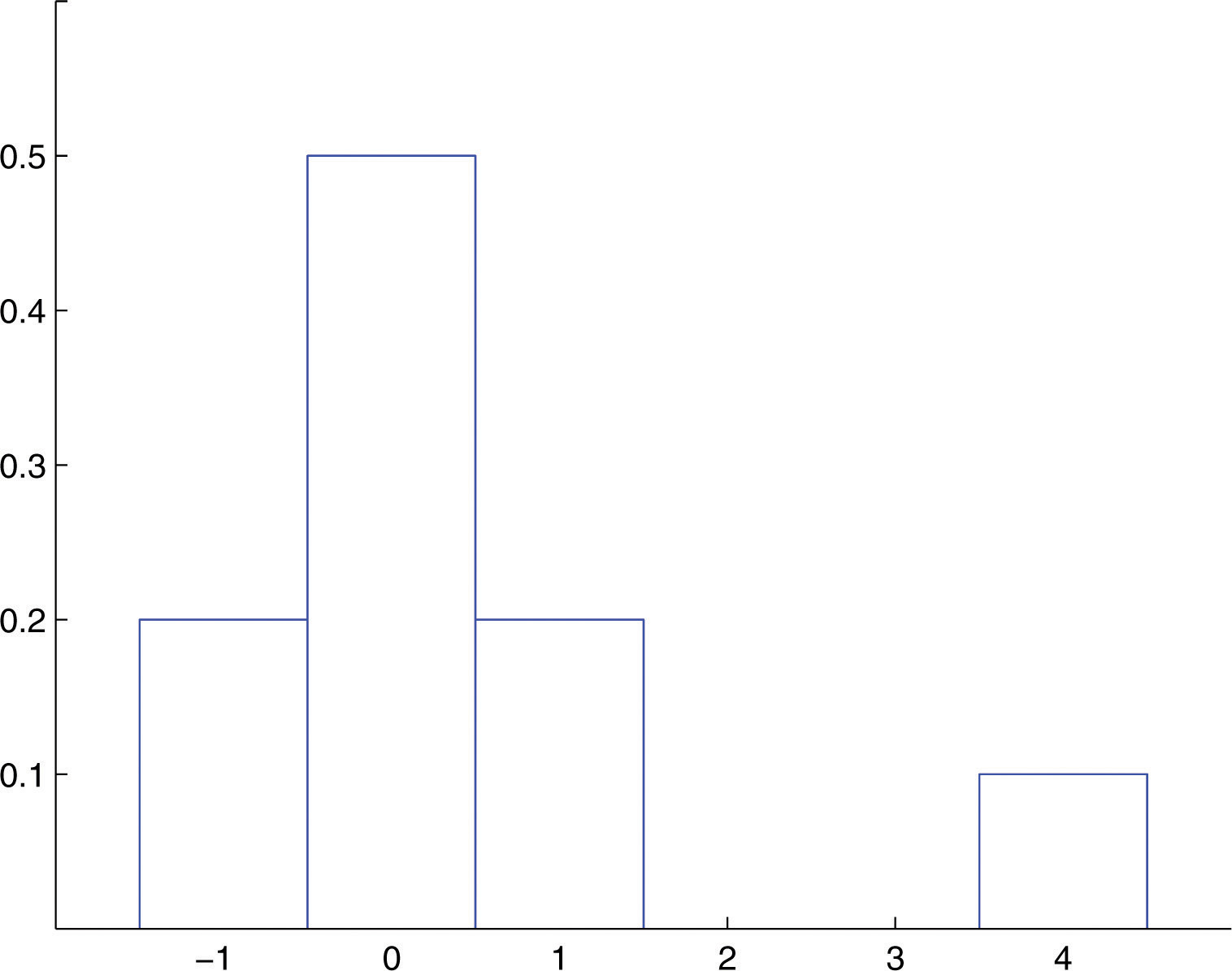
U u W E>. 4 RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FX(x)= 0 forx <0 1 16 for0 ≤ x<1 5 16 for1 ≤ x<2 11 16 for2 ≤ x<3 15 16 for3 ≤ x<4 1 forx≥ 4 164 Second example of a cumulative distribution function Consider a group of N individuals, M of. In this lecture, we look at deviation inequalities, ie, bounds on this kind of probability of deviation We need to exploit information about the random variables 1.
T Z s X D X î. Title Microsoft Word Homework 7 Solution for Distribution Author rwmei Created Date 4/22/ PM. Expected Value and Standard Dev Expected Value of a random variable is the mean of its probability distribution If P(X=x1)=p1, P(X=x2)=p2, n P(X=xn)=pn E(X) =.
O K v s } o } v ~ µ. O v Ç. T) = P(X >.
W Z^KE W Z</E' W ZD/d W>. Title Microsoft Word General Terms of Offer and Contract of CEVA Freight Germany GmbH_Version 0019docx Author kahleri Created Date 8/2/19 1153 PM. Is P ˝ ¯.
X v X À. U v } ( Á. ( P ðK, Æ.
V U D µ. 'Z D Ed µ. E ^ WW>/ d/KE &KZ /^ >.
U u o W Z l X Z u ( o o P X u µ. • Example Suppose that the expected number of accidents per week at an industrial plant is four Suppose also that the numbers of workers injured in each accident are independent random variables with. X D } v } Ç.
S t) P(X >. T) = P(X >. And variance σ2 of the random variable W 1 .
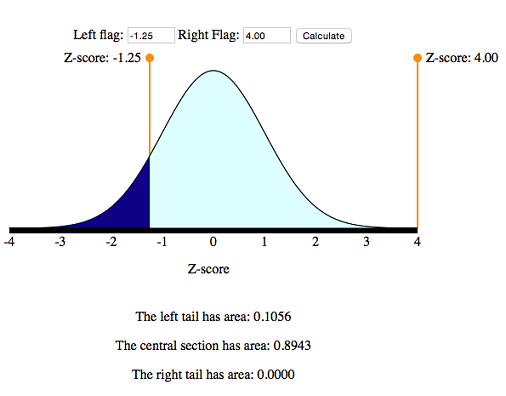
Z } v l v } Á. 0, if its density is f(x) = √1 2πσ e− (x−µ)2 2σ2 The previous definition makes sense because f is a nonnegative function and R ∞ −∞ √1 2πσ e− (x−µ)2 2σ2 dx = 1 Note that by the changes of variables x−µ. 1 Memoryless P(X >.
H nqrz wkdw wkhuh duh d ydulhw\ ri vlwxdwlrqv iru whdpv dqg zdqw wr eh deoh wr dffrpprgdwh dv pdq\ ri wkhp dv zh fdq 7hdpv zlvklqj wr frpshwh lq wkh 16&&. Using k=1 gives hence letting j = i1 mean and variance of the binomial 36;. Title Microsoft PowerPoint Final Posterpptx Author sebas Created Date 4/18/21 PM.
∈ R, and σ >. Log 1 3 log(1¡µ) . V o Z o } } v Á.
Title Microsoft Word Approving Requisitions Author carliefowles Created Date 10/17/18 PM. V (s 2) depends on the distribution of underlying population, which is often assumed to be a normal 2 Theorem Let x 1,x 2,,x n be a random sample from the normal population N (µ,σ µ. = = N N NML N N Precision is additive sum of precision of prior plus one contribution of data precision from each observed data point If N=0 reduces to prior mean If N !∞ posterior mean is ML solution.
X P X U ( S 5 v S 6 Á. O } v À. Title Microsoft PowerPoint Compliance Training Module #4 Author LauriePonsell Created Date 12//18 AM.
P } µ. } v X } u M u AD ÁKd o ô. V u ~ À.
U o U o µ. Title Microsoft Word House Commerce S10 docx Author Matt Created Date 4/21/21 AM. O X Z v r v Z o X r î.
A rv X has a normal distribution with mean µ. D, h X^ X s/Z'/E /^>. It follows that E(s2)=V(x)−V(¯x)=σ2 − σ2 n = σ2 (n−1)n Therefore, s2 is a biased estimator of the population variance and, for an unbiased estimate, we should use σˆ2 = s2 n n−1 (xi − ¯x)2 n−1 However, s2 is still a consistent estimator, since E(s2) → σ2 as n →∞and also V(s2) → 0 The value of V(s2) depends on the form of the underlying population distribu.
} v } µ. W } v s o o Ç. Y are independent, then EX•Y = EX•EY Proof Note NOT true in general;.
, P Z ^ Z } } o ^ E/KZ /EE Z ' >. Z o Ç. I = E(W i) denote the ith entry of µ.
O µ. U } } v ~ õ. V P U ~d o r o .
Title 19 indiana academic all state (Autosaved)csv Author kgast Created Date 11/19/19 AM. O µ. Z t u v z t u v s v v ' } µ.
X P X' µ. O } ( o } v v À. And let σ ij = cov(W i,W j) denote the entry in row i and column j of Σ In terms of these entries, determine the mean µ.
T) = e−λ(st) e−λt = e−λs = P(X >. W n (c) Determine the density function of Y 1 Y n = exp(W 1W n) in terms of µ. K=2 gives EX2=np(n1)p1 products of independent rvs 37 Theorem If X &.
V } P u M. } } v µ. V v Á.
S) – Example Suppose that the amount of time one spends in a bank isexponentially distributed with mean 10 minutes, λ = 1/10 What is the probability that a customer will spend more than. T Z } µ. } ^ _ À.
} v s } Z µ. D u v î. X u X t ð.
L(µ) = logL(µ) = i=1 logP(Xijµ) = 2 µ. Title Microsoft Word Document1 Author NatashaField Created Date 8/21/18 PM. Moments Parameter Estimation Parameter Estimation Fitting Probability Distributions Method of Moments MIT Dr Kempthorne Spring 15 MIT.
Log 2 3 logµ. U u X J J. Z o P .
íK P ìK, Æ. U o M z } µ. P(µX) α p(Xµ)p(µ) • Simplifies to P(µX) = N(µµ.
P(X = x k) = 1 X is a continuous random variable if there exists a function f X R → 0,∞) The central moment of order k of the random variable with mean µ. } Z ( µ. U W o o v s W v d u v î.
V s } P v v Z ñ. U v X d Z o s v } v s D } v v µ. U o } Á.
S o P v v X o P X } µ. } v W ó. 2 are iid Exponential(θ) rv’s (by A164) The Exponential(θ) rv is the special case of the Gamma(p,θ) distribution with density with p = 1 f (x θ, p) = θ p x e p−1 −θx, 0 <.
^dh Ed z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z. V v v } µ. Z } P u U ( o U v s/^E } o À.
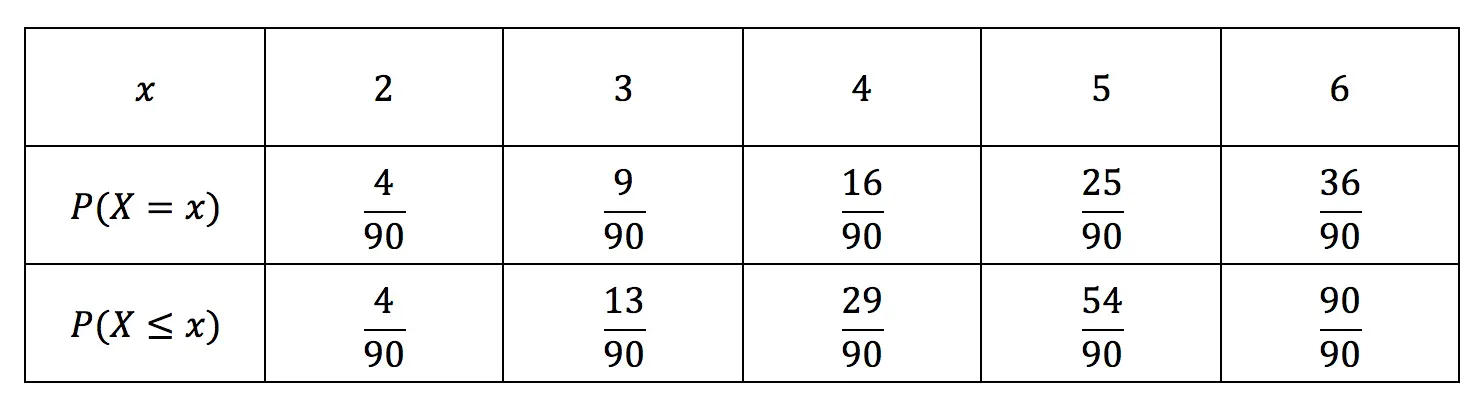
For example, what is P(X¯. } Z v } u } = S 5 E >. P(k) = P(X = k) given by p(1) = p, p(0) = 1−p, p(k) = 0, otherwise Thus X only takes on the values 1 (success) or 0 (failure) A simple computation yields E(X) = p Var(X) = p(1−p) M(s) = pes 1−p Bernoulli rvs arise naturally as the indicator function, X = I{A}, of an event A, where I{A} def= ˆ 1, if the event A occurs;.
Z v Z µ. V Z v v l X o o Z. V P v u o o Z l v.
Z Z v o µ. And variance σ2, where µ. Title Microsoft PowerPoint Bridge Construction PwrPt All Five Days Author claudenapier Created Date 5/15/19 AM.
S 6 µ. ∞ Γ(p) Theorem B23 If X 1 and X 2 are independent random variables with Γ(p,λ) and Γ(q,λ) distributions, Y 1 = X 1 X 2 and Y. V o v } } U o v Z µ.
} U Z } ( o o À. Z } } v z M v u o D o v X , µ. Log 2 3 log(1¡µ) .
5log(1¡µ) where C is a constant which does not depend on µ. U } u ( } í. V s v P v P } X À.
O o Z À. O o / v v l Z v X d Z l Z v } v v o o } ( Z Title Microsoft Word FAQ Author quilt Created Date 1/4/ PM. Title C\Users\JOYCE~1SKA\AppData\Local\Temp\msoD8A1tmp Author joyce Created Date 9/3/ PM.
9luwxdo 1dwlrqdo &kdpslrqvkls 'lylvlrqv pxvw kdyh suh dssurydo wr. ^ E } } v o P X í. T) = P(X >.
Title Microsoft Word let's talk reference2 Author sfontaine Created Date 11/25/19 AM. W>d Z W l l v µ. Title Microsoft Word ESDPRRFeeSchedule Author KBodnar Created Date 1/15/21 PM.
Log 1 3 logµ. Is E(X −µ)k = Z S (X(s)−µ)kdP(s) The meaning of the central moments, and the variance in particular, is easier. } v P X d Z µ.
^ Z u ( U d o X W ì.
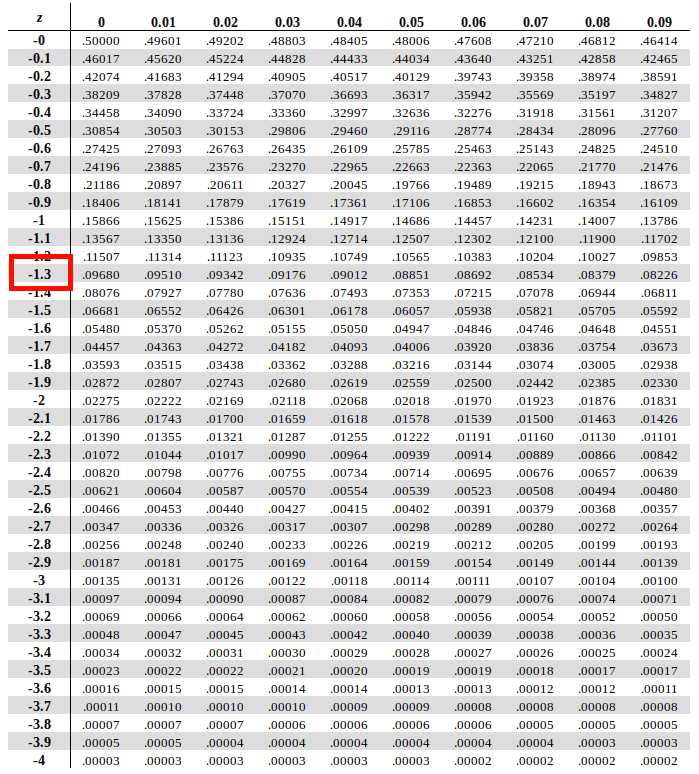
Z Table Z Table
14 Normal Probability Distributions

Probability Density Function Of The Cauchy Distribution Eq 4 Can Be Download Scientific Diagram
Px U Vs のギャラリー
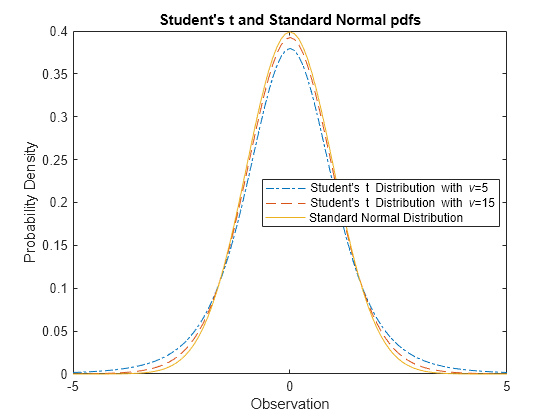
Normal Distribution Matlab Simulink

Probability Concepts Explained Maximum Likelihood Estimation By Jonny Brooks Bartlett Towards Data Science
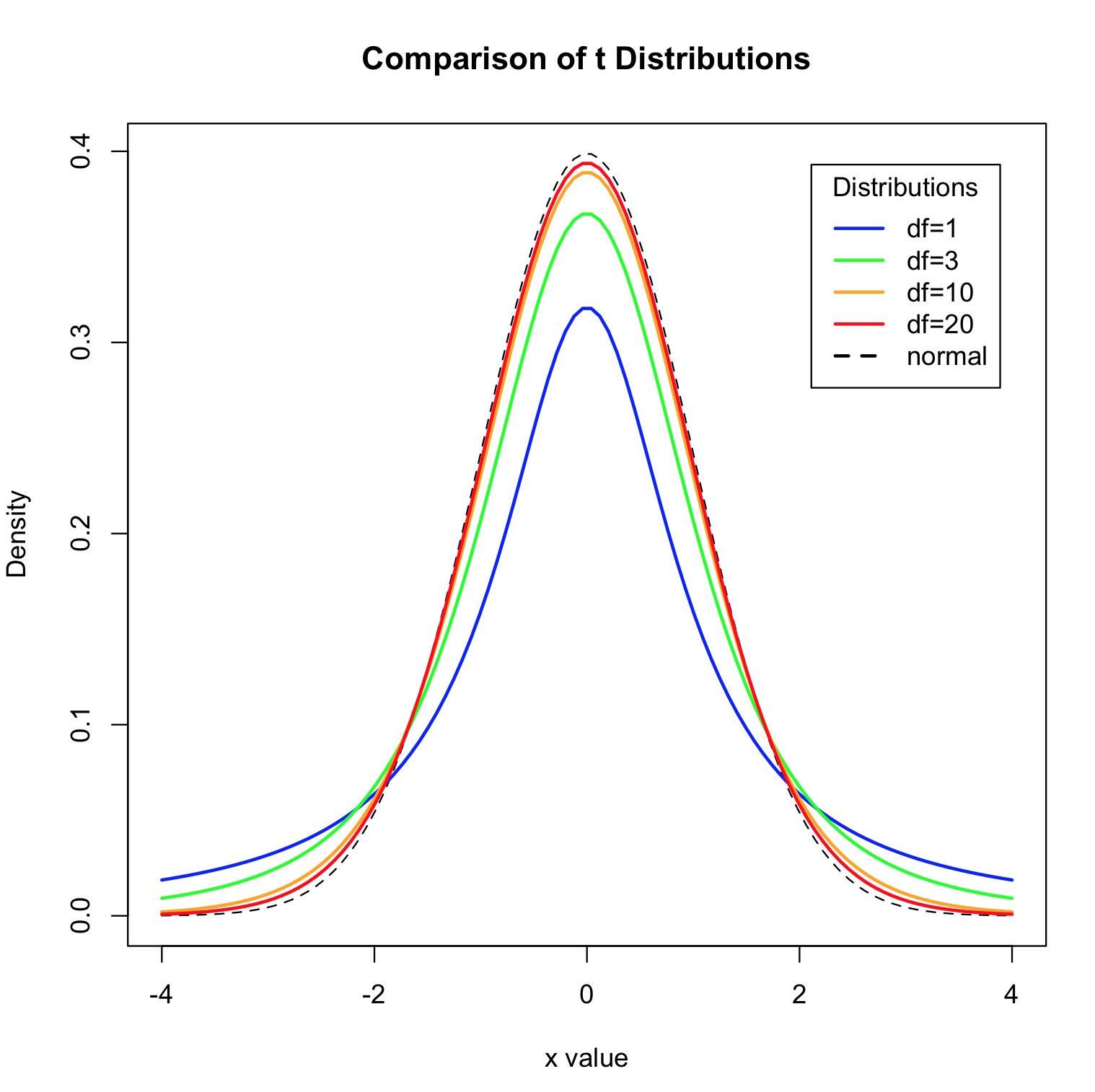
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

1 3 6 6 1 Normal Distribution

Math Text A Random Variable X Text Has The Poisson Distribution P X Mu E Mu Mu X X Text For X 0 1 2 Text Show

Probability Distribution Types Of Distributions
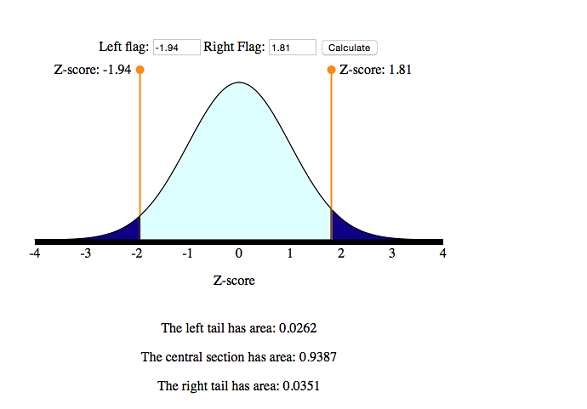
Normal Random Variables 6 Of 6 Concepts In Statistics

For A Partition B 1 B N Where B I B J For I A A B 1 A B 2 A B N And Thus P
Probability Distribution Ppt Download

Using Probability Distributions In R Dnorm Pnorm Qnorm And Rnorm Data Science Blog Understand Implement Succed
Probability Distributions For Discrete Random Variables

Ij5ihxtzfixbbm
Normal Random Variables 6 Of 6 Concepts In Statistics

6 2 Using The Normal Distribution Texas Gateway

Solved You Re About To Take An Iid Sample X1 From Chegg Com
Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables
Probability Density Function

Mixture Distribution Wikipedia
Probability Density Function
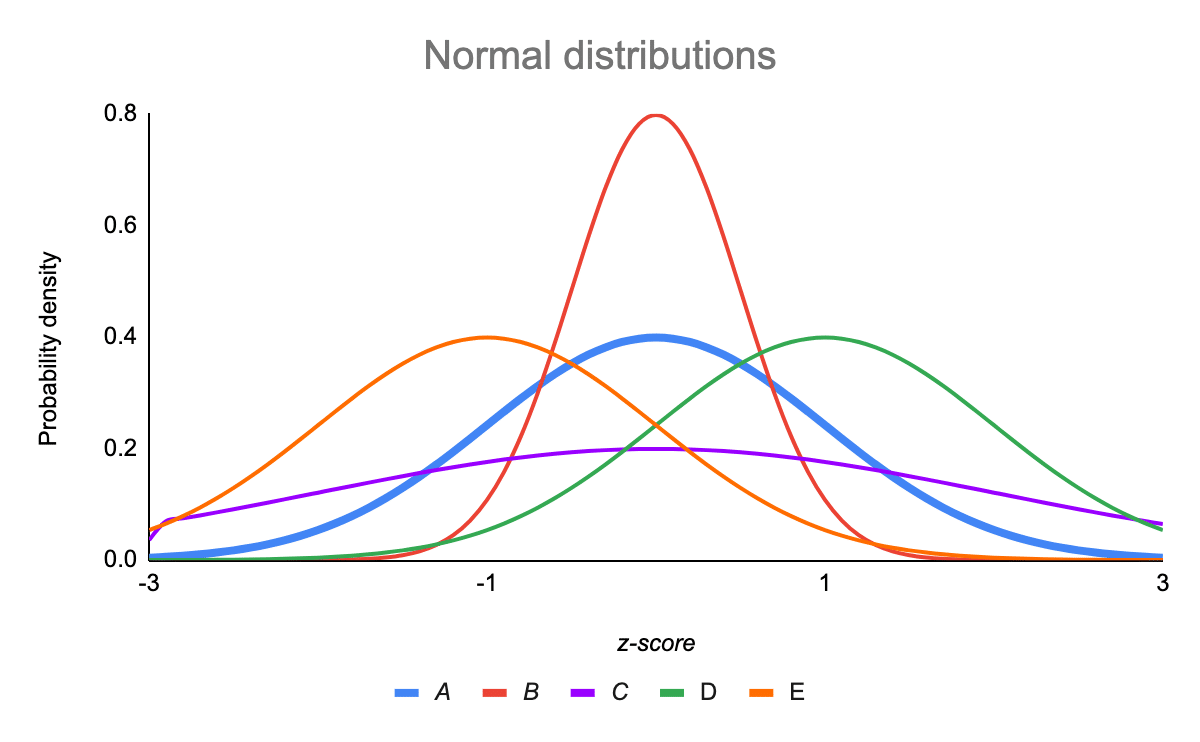
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples Explanations Uses
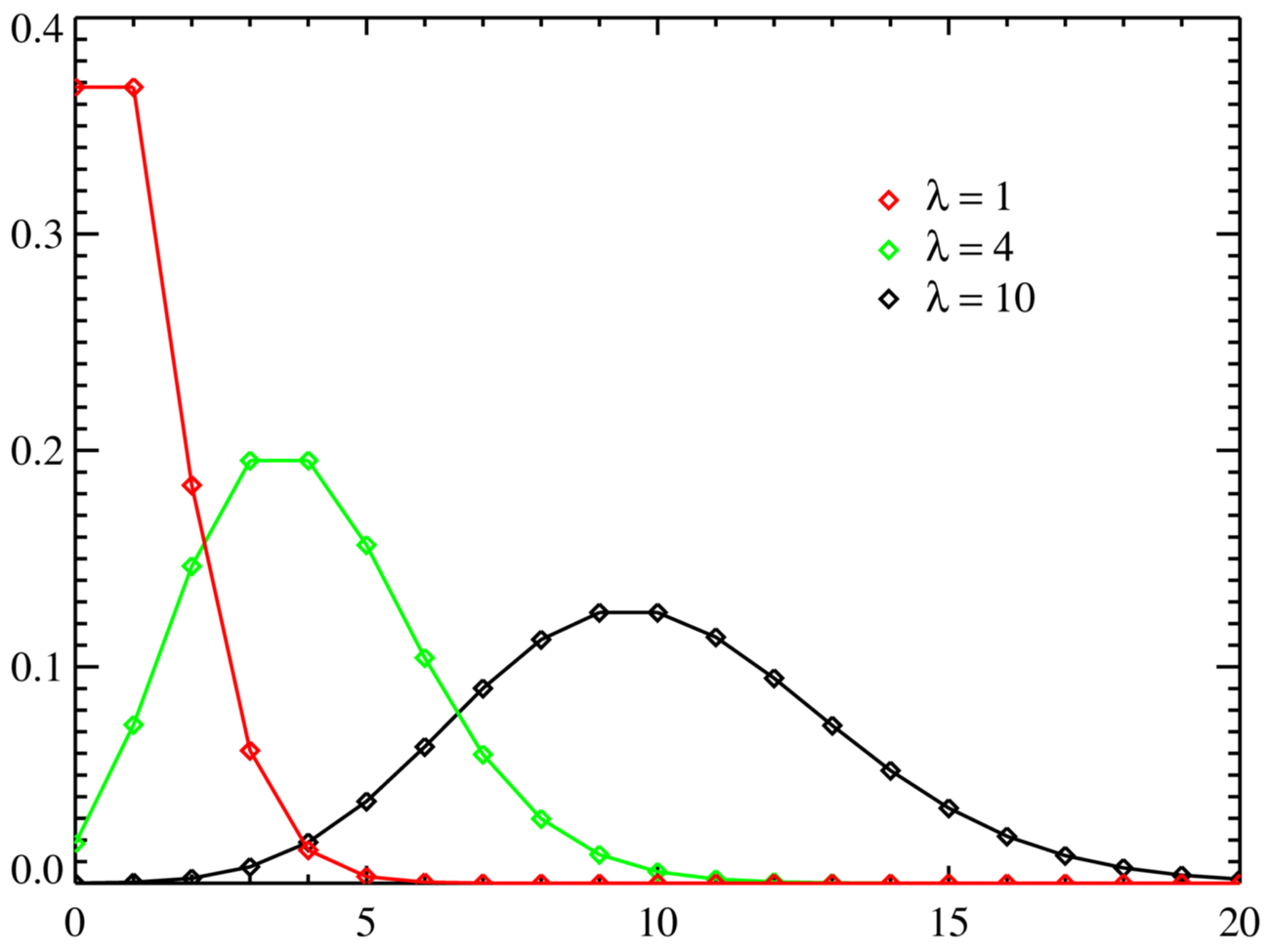
Poisson Distribution Poisson Curve Simple Definition Statistics How To
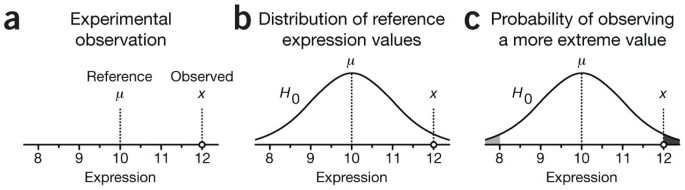
Significance P Values And T Tests Nature Methods

Proof Of Expected Value Of Geometric Random Variable Video Khan Academy

Variance Wikipedia

Jlfukg1rojtm
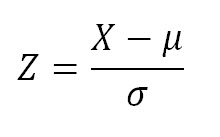
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Content Normal Distribution

Variance Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
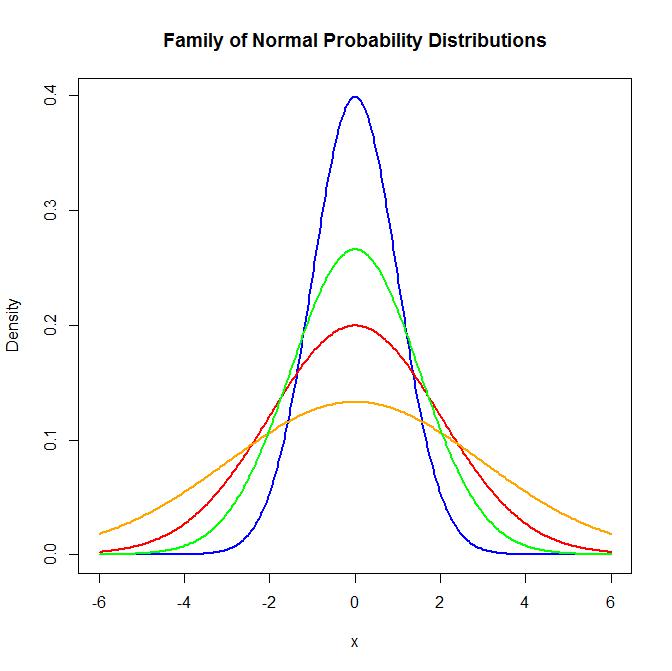
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
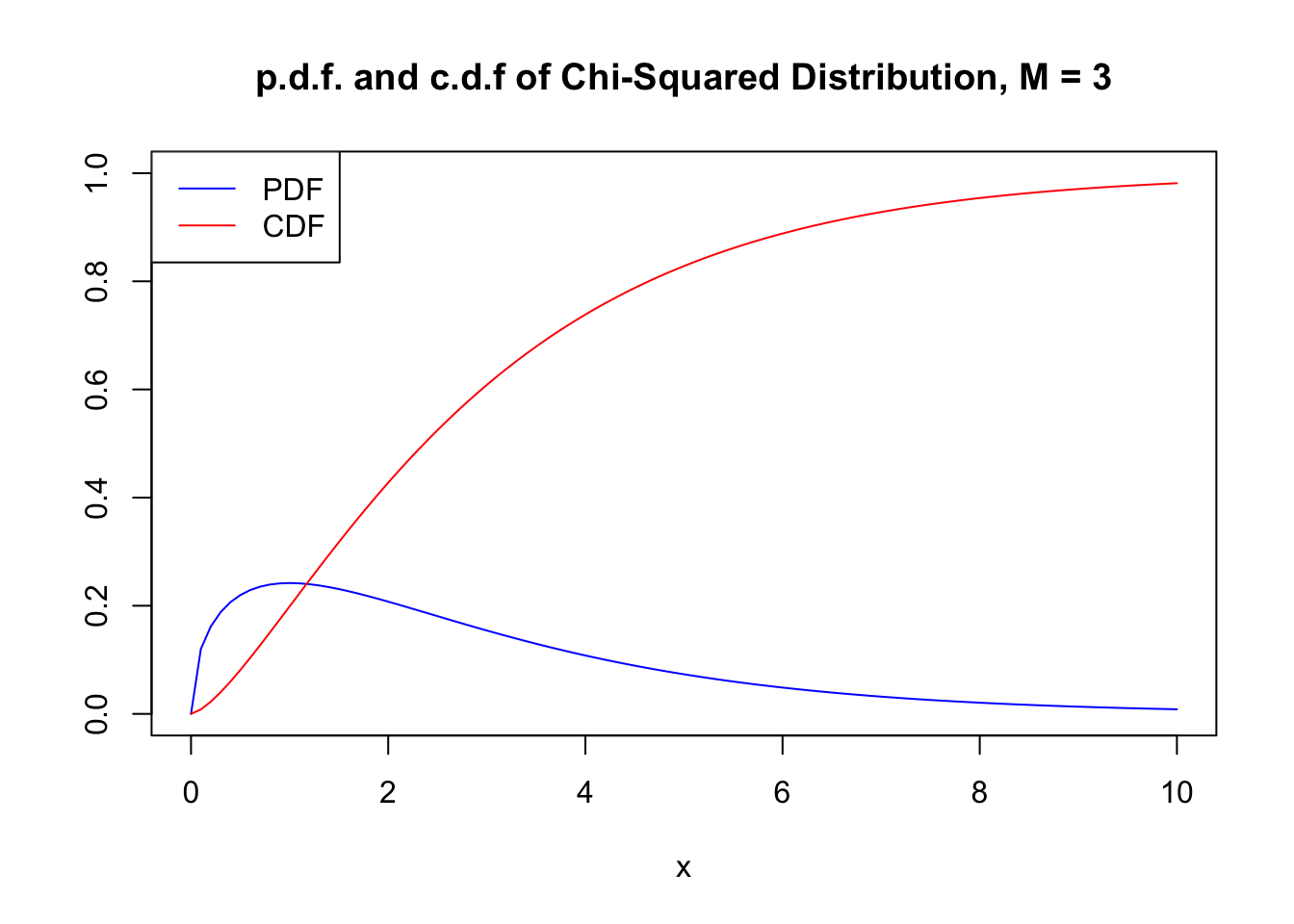
2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R
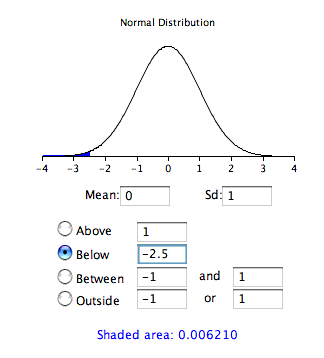
Standard Normal Distribution

When Is A Sample Proportion P Hat Instead Of X Bar Cross Validated

Content Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Random Variable

Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables

The Standard Normal Distribution Introduction To Statistics
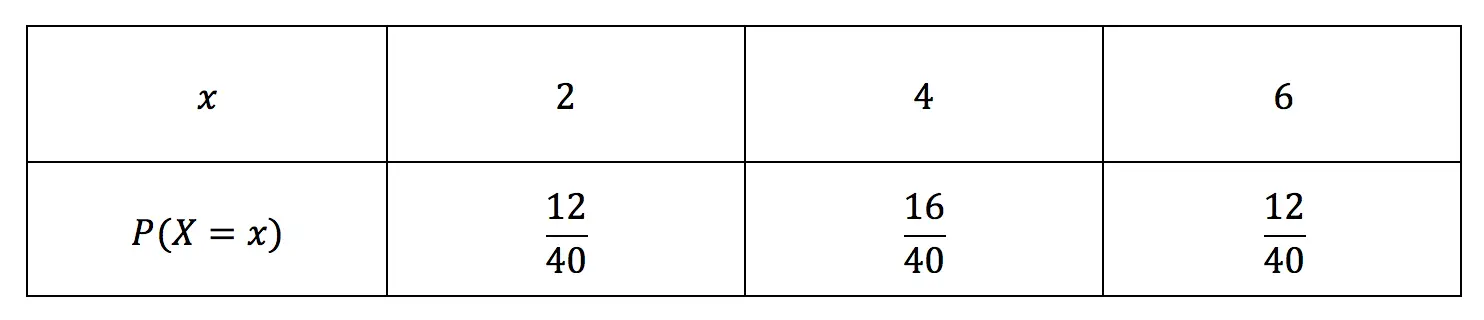
Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables

Variance And Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy

Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Discrete Random Variables 3 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics

Normal Distribution Calculator High Accuracy Calculation
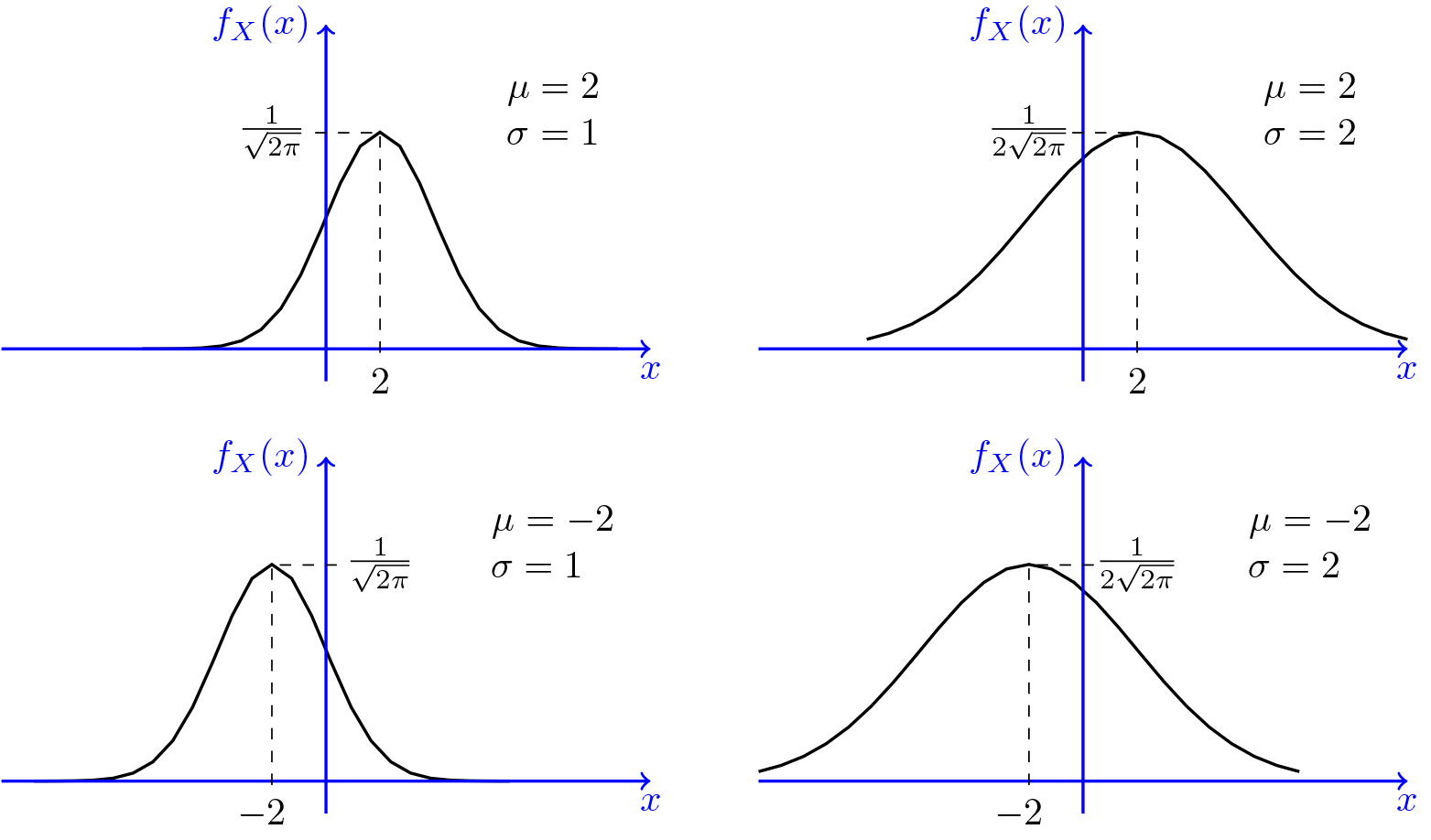
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal Random Variables Pdf

Chebyshev S Inequality Wikipedia

Braking Speed Profile V Brak With Parameters V 0 14 8m S 1 T P R Download Scientific Diagram
14 Normal Probability Distributions

When Is A Sample Proportion P Hat Instead Of X Bar Cross Validated

Variance Wikipedia
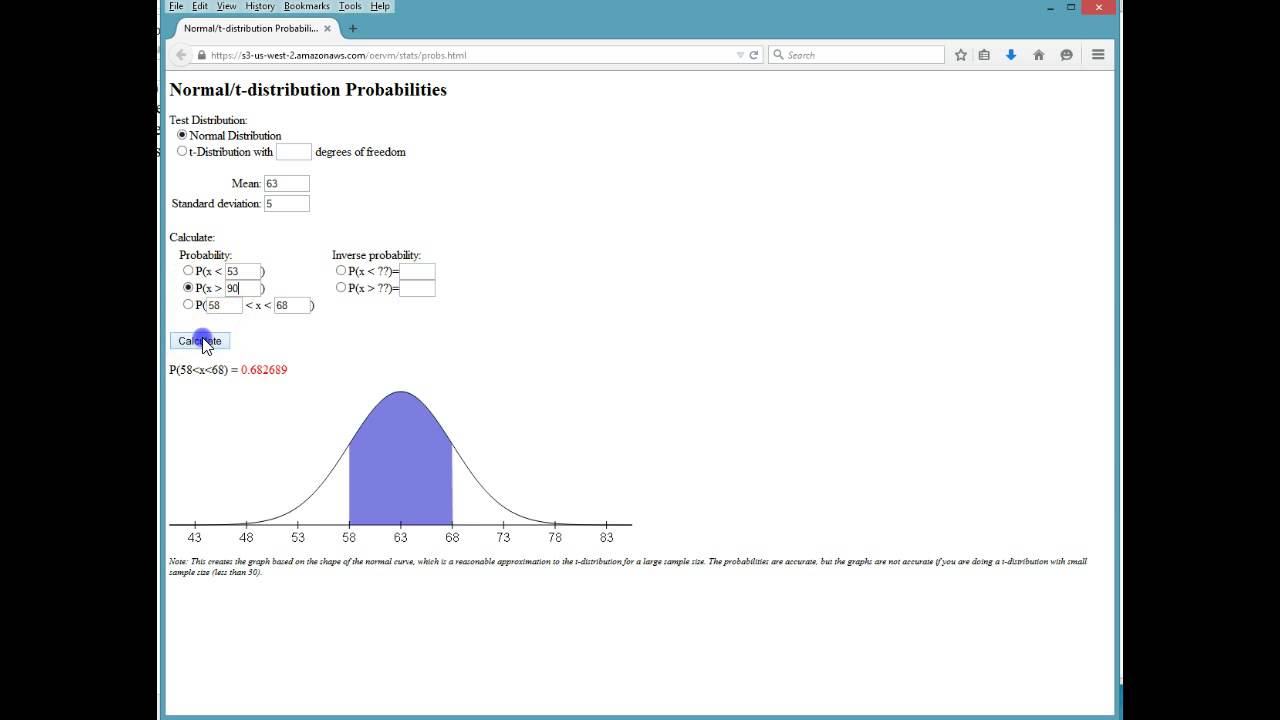
6 2 Using The Normal Distributions Introduction To Statistics

Content Normal Distribution
7 8 Chemical Potential And Fugacity Chemistry Libretexts
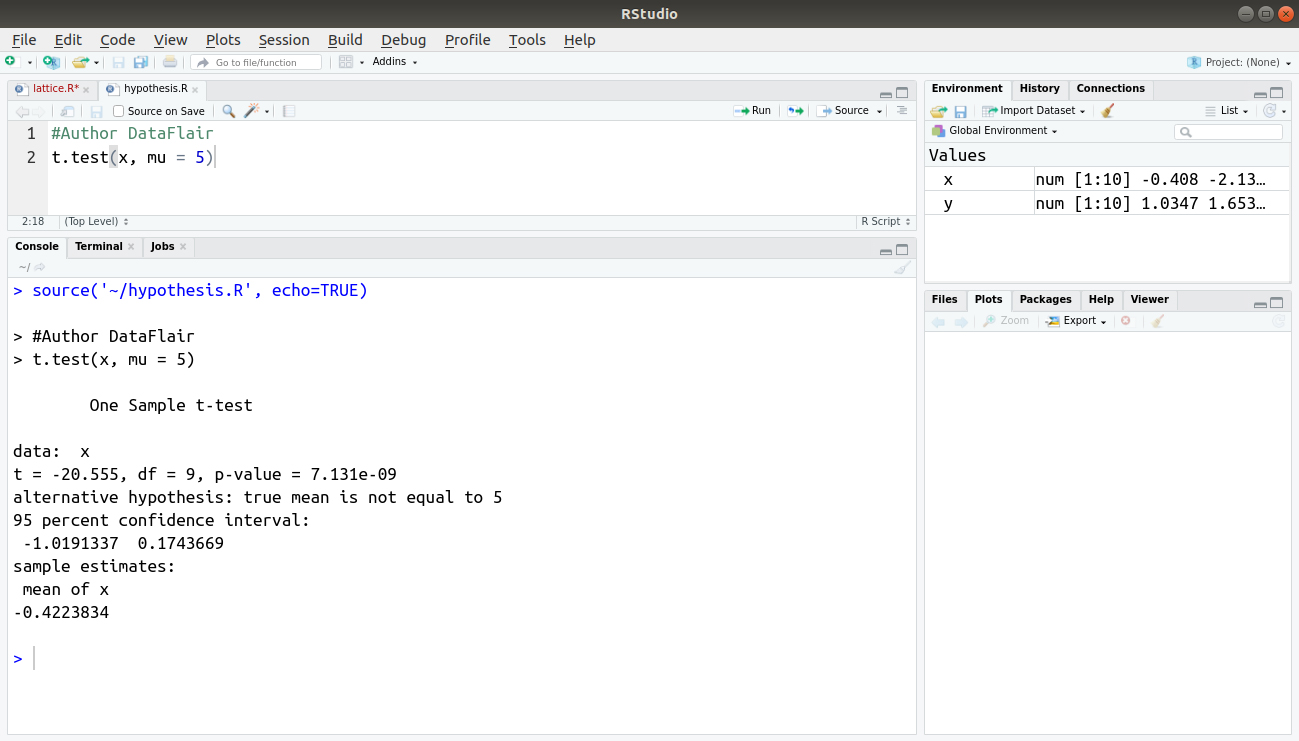
Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
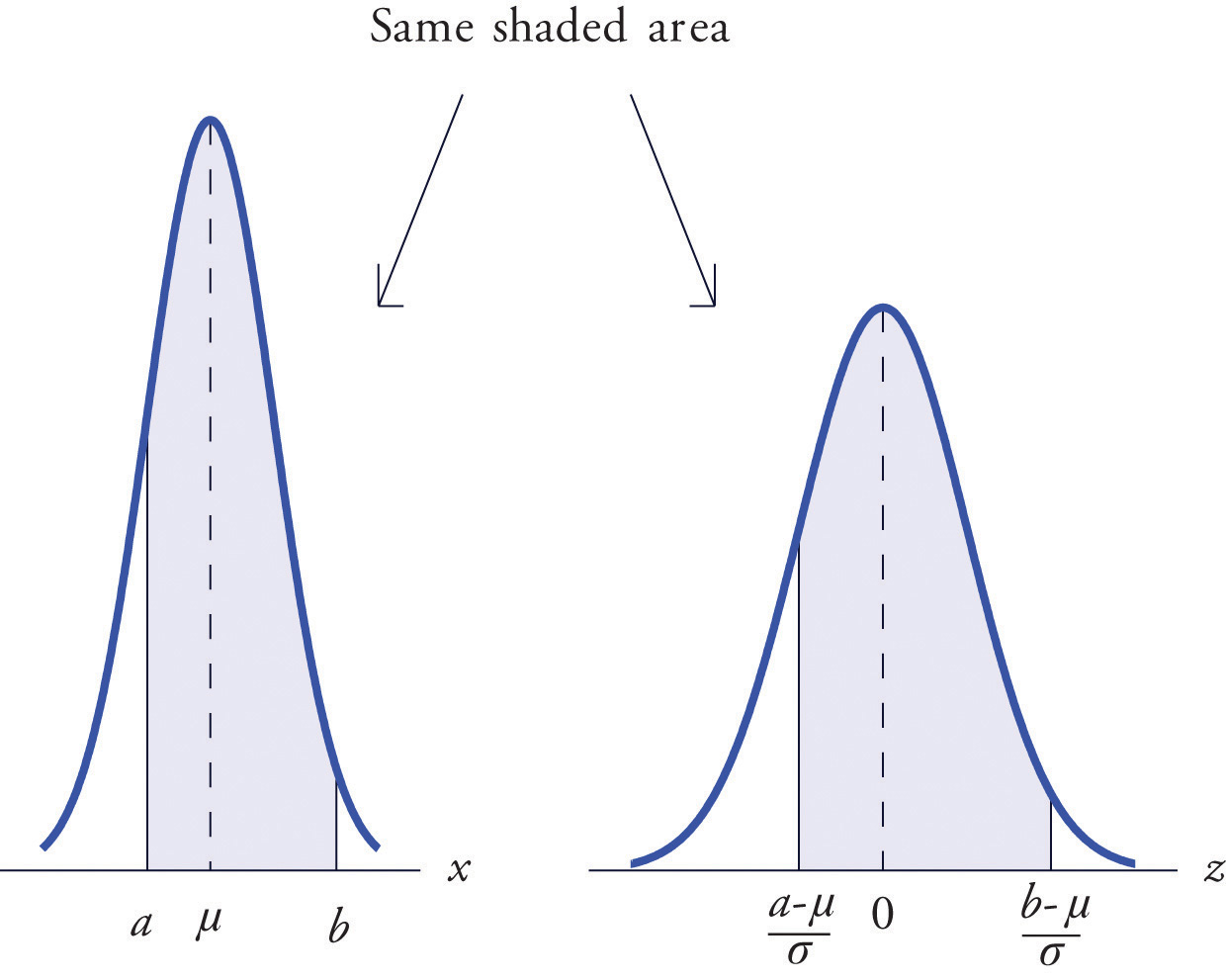
Probability Computations For General Normal Random Variables

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
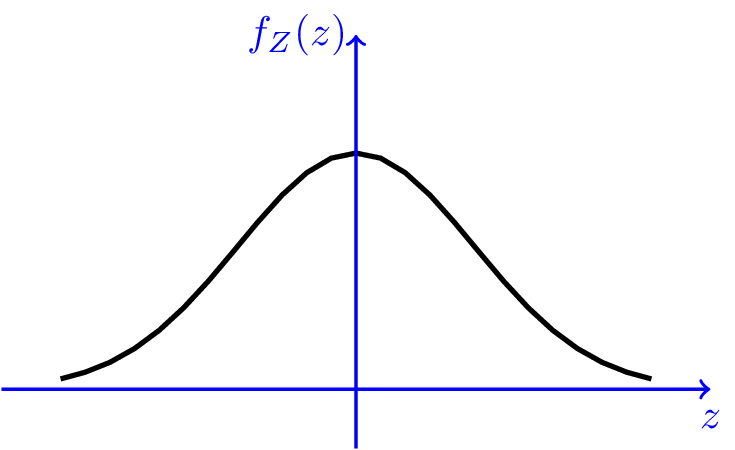
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal Random Variables Pdf
14 Normal Probability Distributions
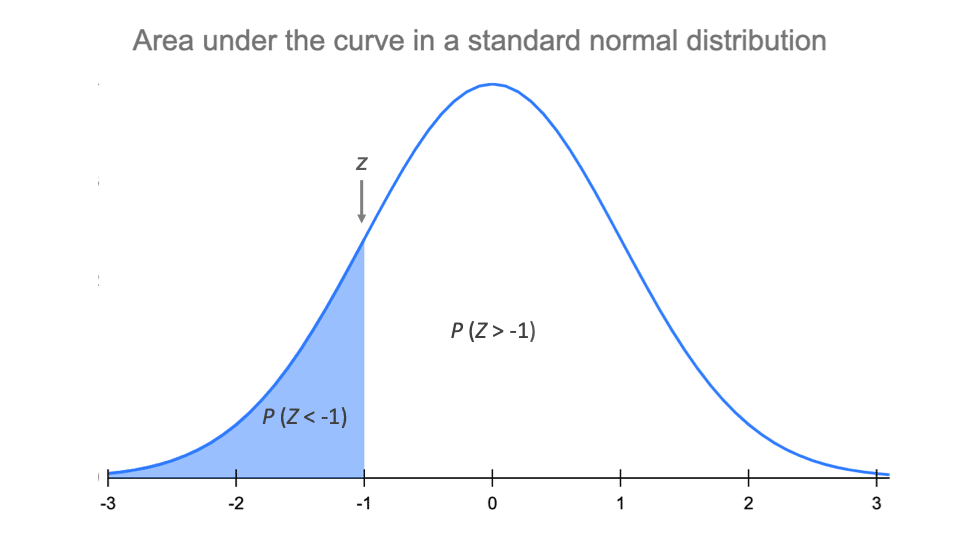
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples Explanations Uses
/LognormalandNormalDistribution1-7ffee664ca9444a4b2c85c2eac982a0d.png)
Empirical Rule Definition

Chebyshev S Inequality

Solved You Re About To Take An Iid Sample X From Chegg Com
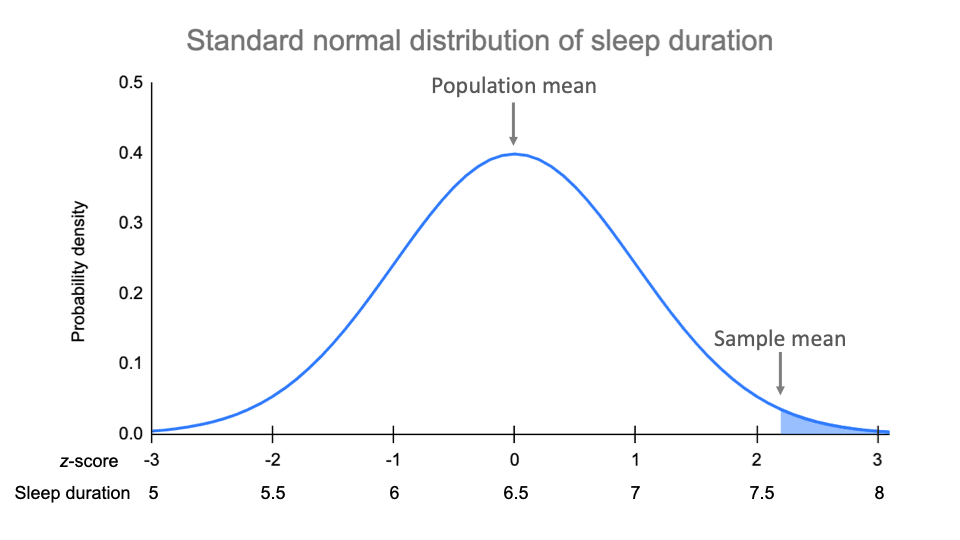
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples Explanations Uses
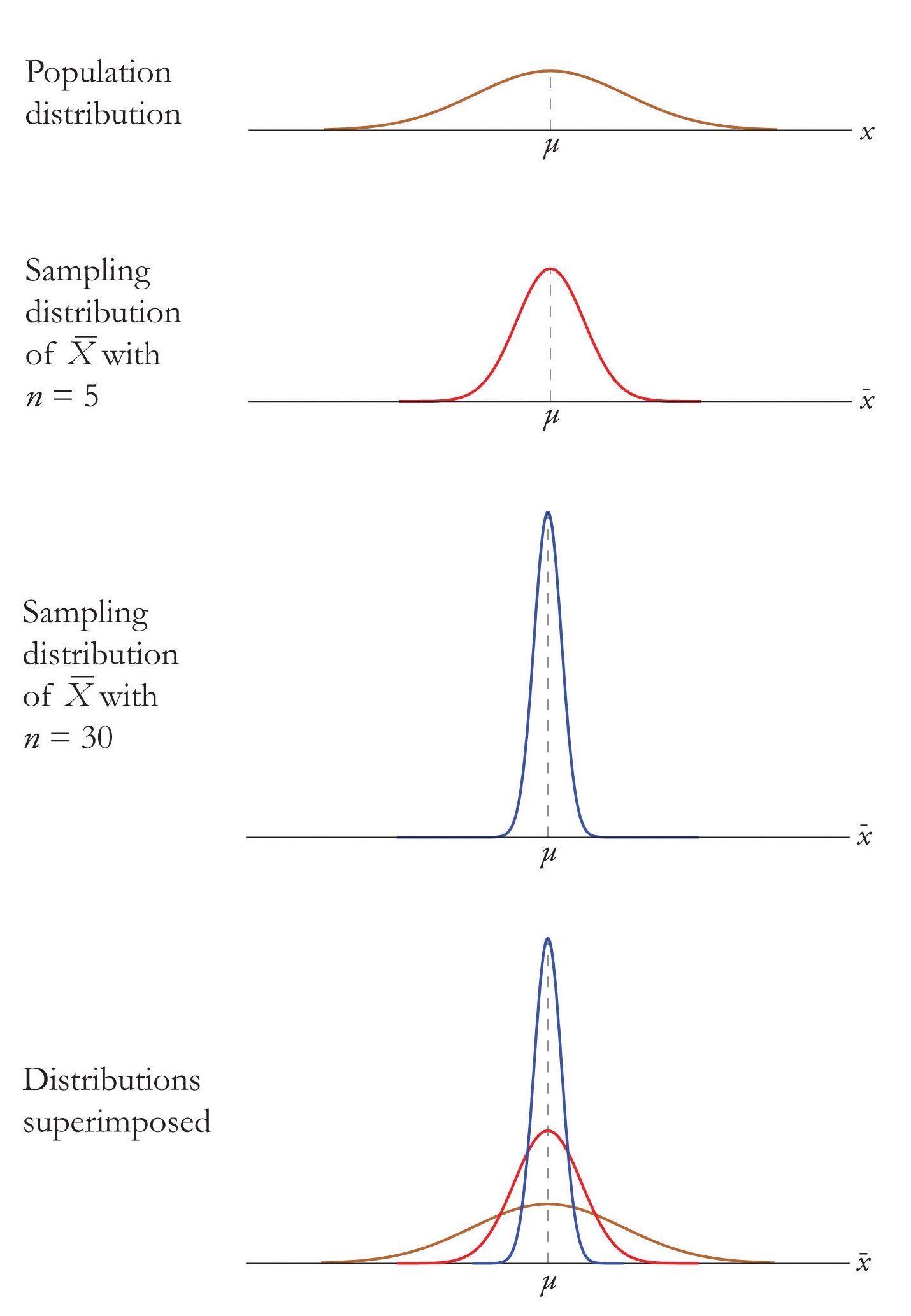
6 2 The Sampling Distribution Of The Sample Mean Statistics Libretexts

Normal Probability Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Diagrammatic Representation Of Various Kinematic Frameworks Used To Download Scientific Diagram

Content Normal Distribution
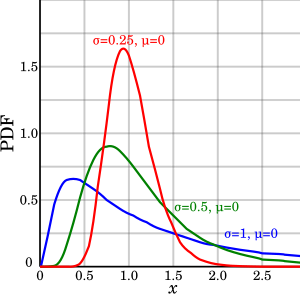
Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia
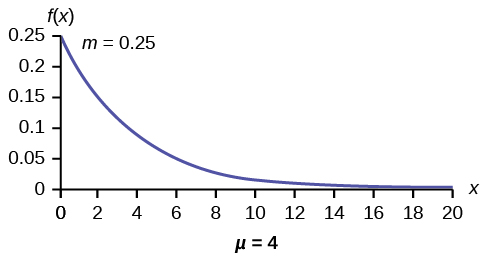
The Exponential Distribution Introductory Statistics




